Expanding new possibilities through development of decorative embroidery into functional embroidery
With today’s 100-year lifespans, people want to continue enjoying happy, healthy lives. At Tajima, we aim to contribute in the healthcare and infrastructure domains with the embroidery technologies we have developed since our founding and help people continue to lead healthy, fulfilling lives. Not only does embroidery add decoration, but it can also be sewn onto materials and used to create preforms, making it valued for its functionality.
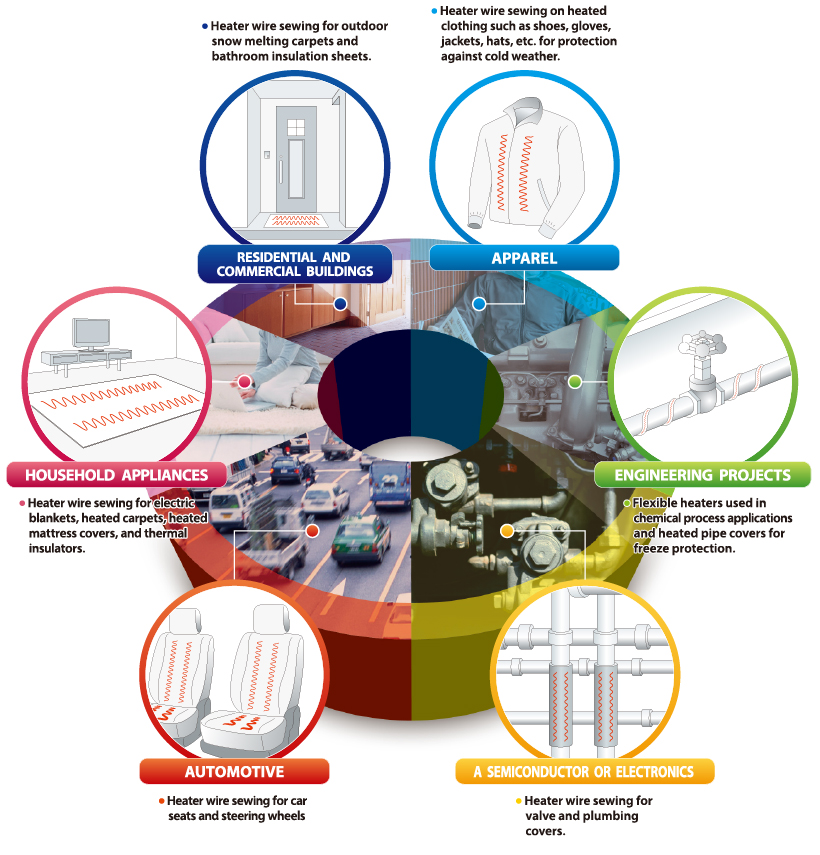
For example, using sewing technology on corded materials can bring greater convenience in various areas of daily life, such as with smart textiles or prevention of frozen pipes.
We expect embroidery technology will be tapped into even more in the future, for example in robotics and the medical field, and that Tajima will contribute to future developments while placing no limits on embroidery technology’s potential.
Embroidery technology promoting healthier, safer lives
Tajima envisions contributing to the medical and healthcare fields by applying our embroidery technology to wearable devices, children’s rehabilitation equipment, assistive products, and more.Smart textiles refer to textile products made from woven or knitted fabrics that feature functions such as gathering biometric data. As the global market grows, this field is expected to continue expanding in the future.
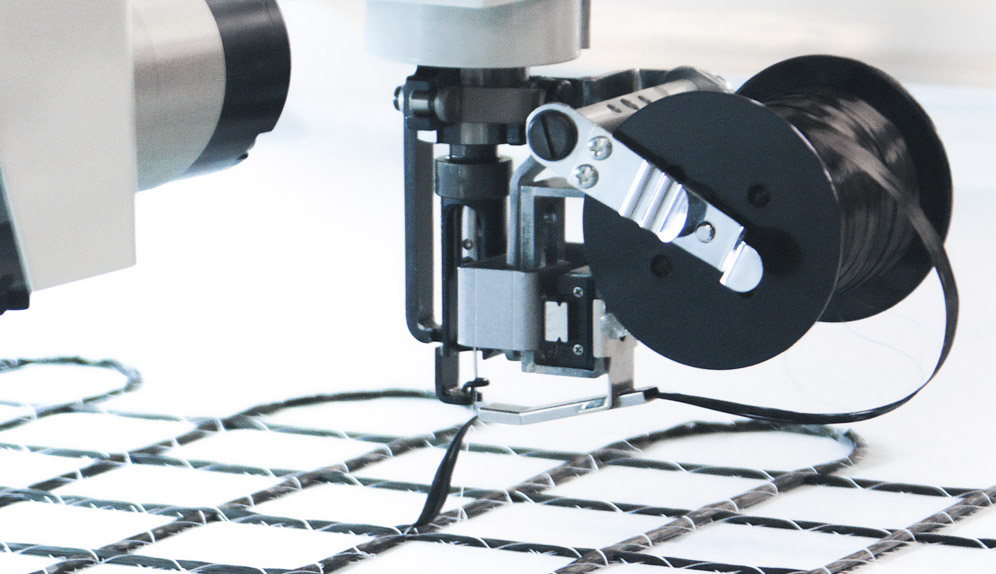
The Tajima Group has extended the sewing technologies we’ve developed over many years to produce a technology—embroidering with electrically conductive thread—that can be applied to electrical wiring systems and sensors.

Example of sewing on items with conductive thread
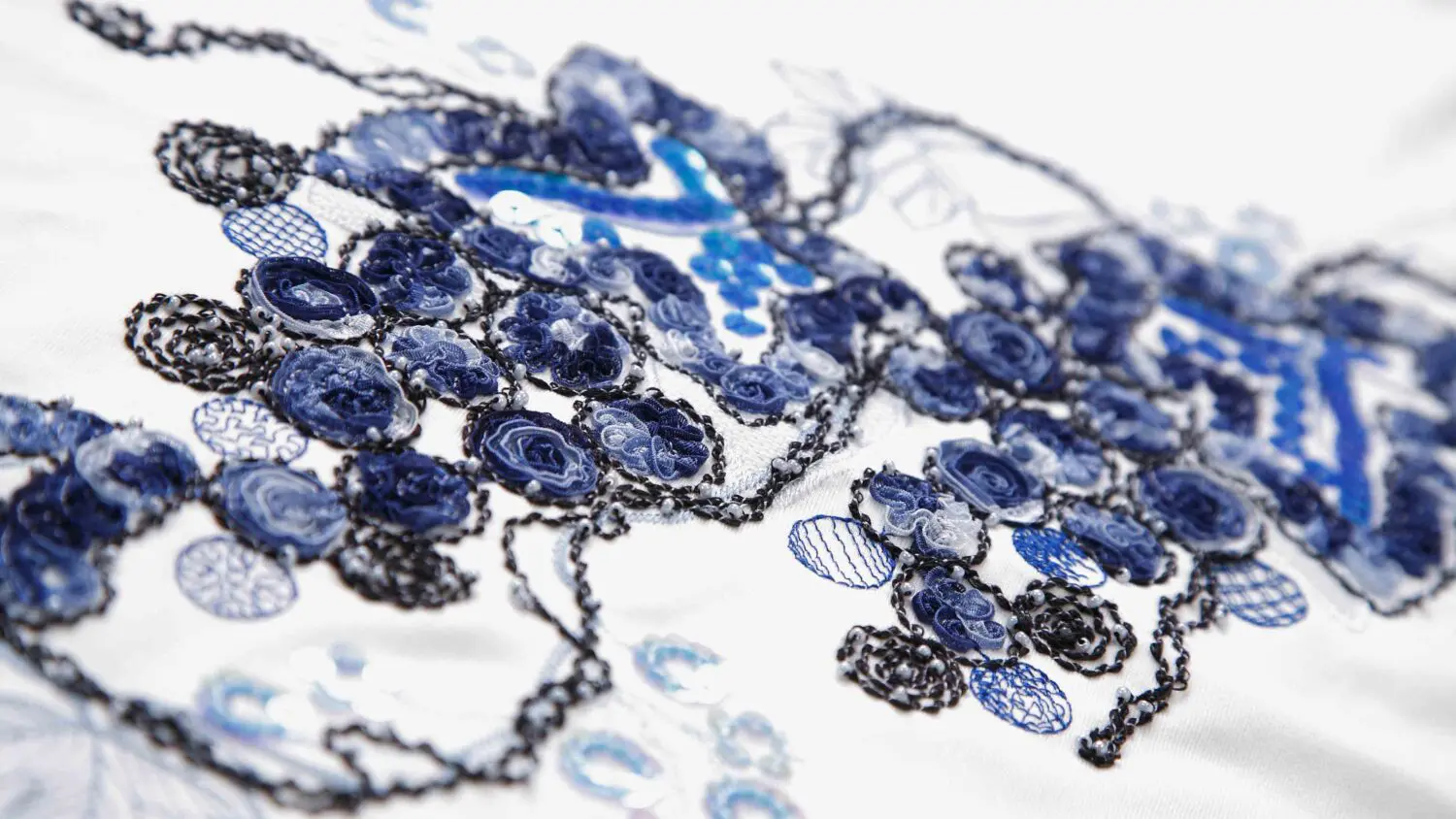
Tajima’s embroidery machines can be used to embroider conductive thread to produce wearable products, such as inner wear with biometric sensors. Tajima machines can be used not only for functional purposes but also for decorative embroidery, permitting applications and designs that are up-to-date with current trends while maintaining functionality.

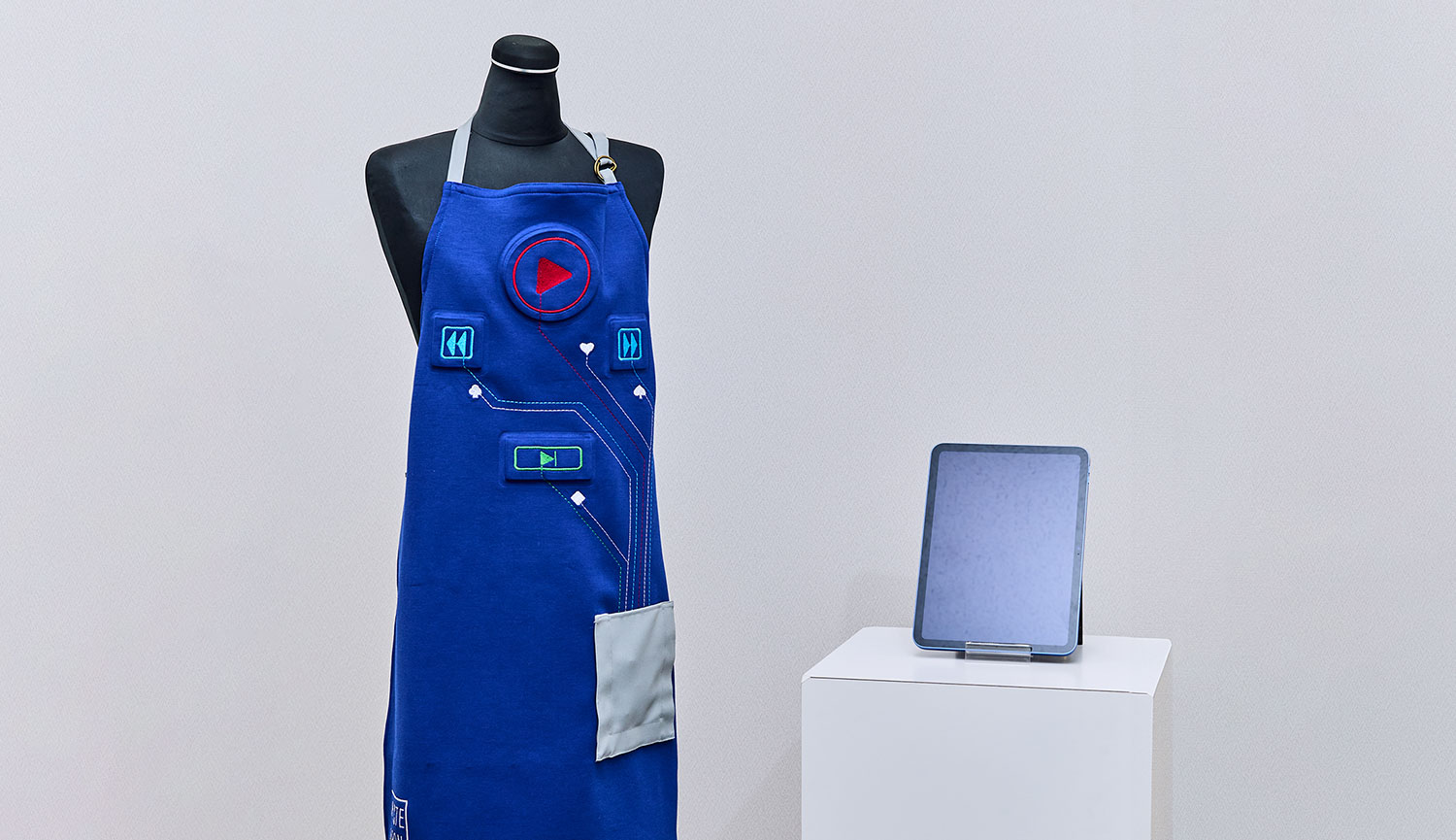
Example of sewing on an embroidered pressure sensor
A pressure-detecting mechanism can be constructed by taking two embroidered electrodes (capacitors) and measuring the change in capacitance resulting from changes in the gap between the electrodes. Pressing the electrodes decreases the distance between them, thereby increasing the capacitance, and the pressure is determined from that change. Sewn onto a product, such as a chair or bed, this sensor can detect whether someone is standing or sitting. Such sensors can be used in nursing care products.
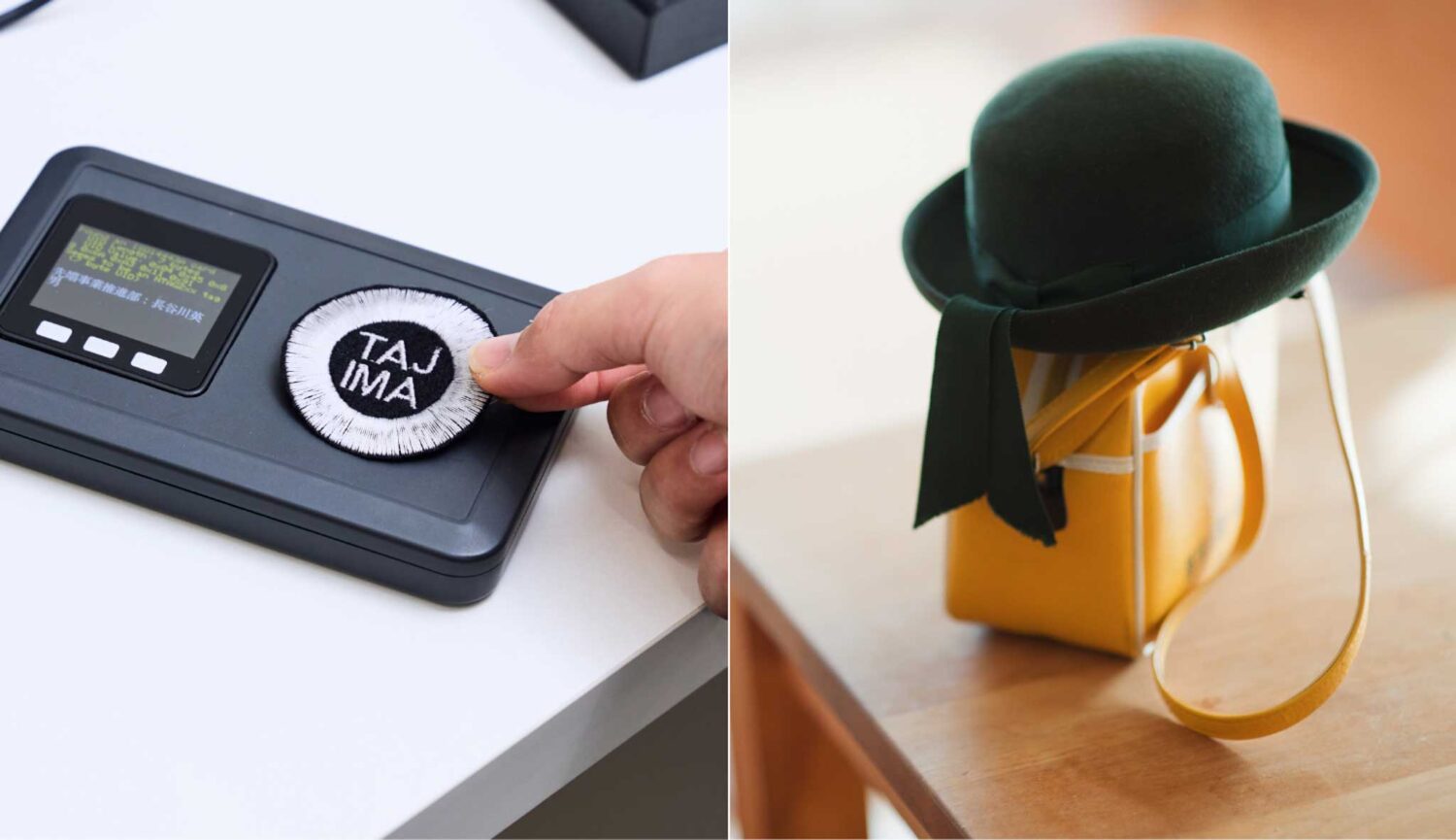

Example of sewing on an RFID
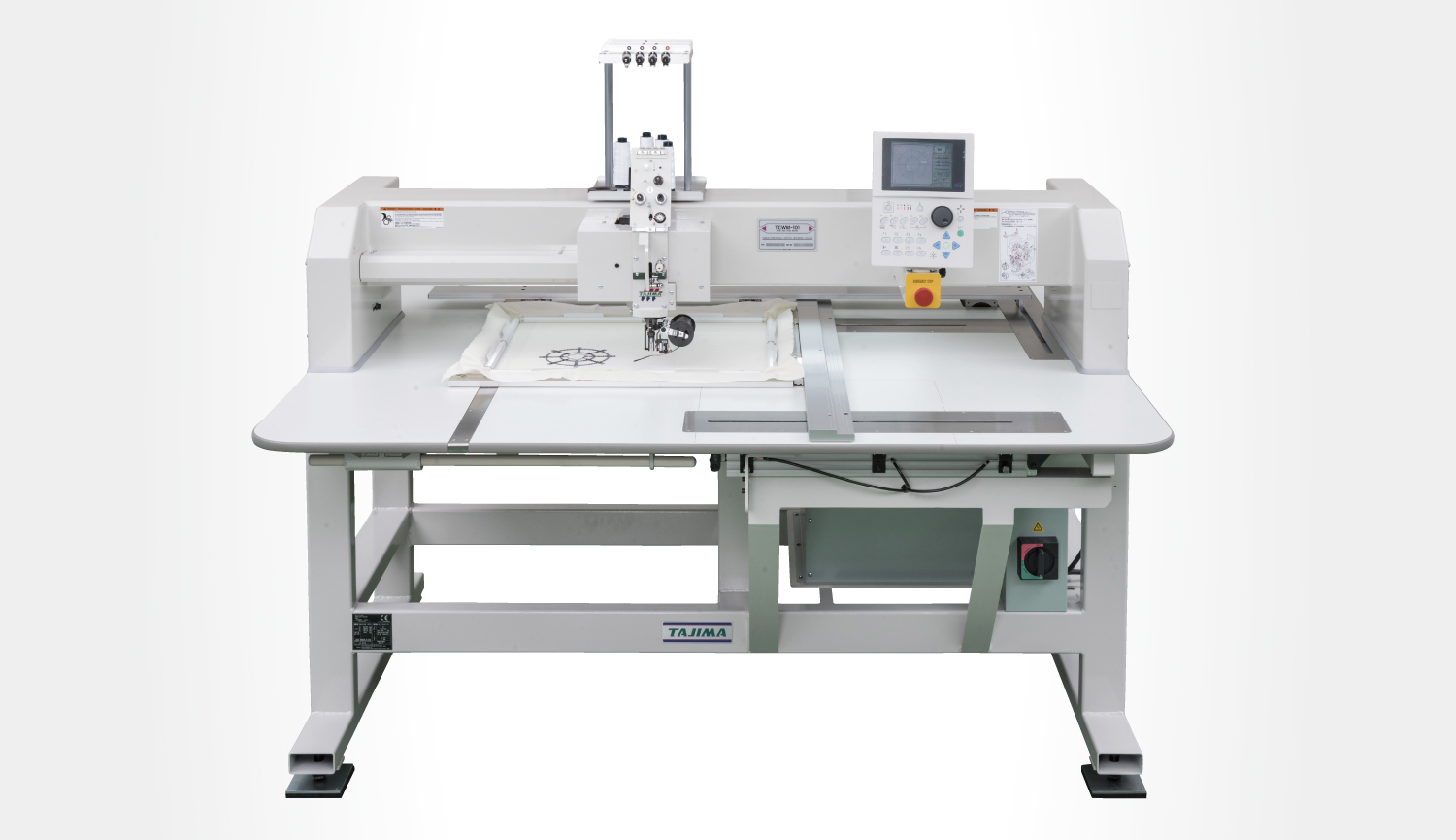
Conductive threads can also be used to orient radio frequency identification (RFID) tag antennas. For example, RFID linen tags can be created using one of Tajima’s “TLMX” series embroidery machines, which are capable of sewing antenna wires. These tags can then be sewn onto uniforms for use as ID cards, with no need to carry an actual card. They can be used in schools, including nursery schools, offices, and any other venue requiring ID.
Supporting sustainable societies with embroidery technology
Tajima aims to utilize the embroidery technologies we have developed over the years in helping solve issues threatening the future of the earth that cannot be ignored. Issues that include energy, the infrastructure supporting the basics of modern life, and measures to deal with natural disasters, which have been occurring more frequently in recent years. As a leading company in the embroidery industry. Tajima is proactive in working to bring about a more prosperous society.
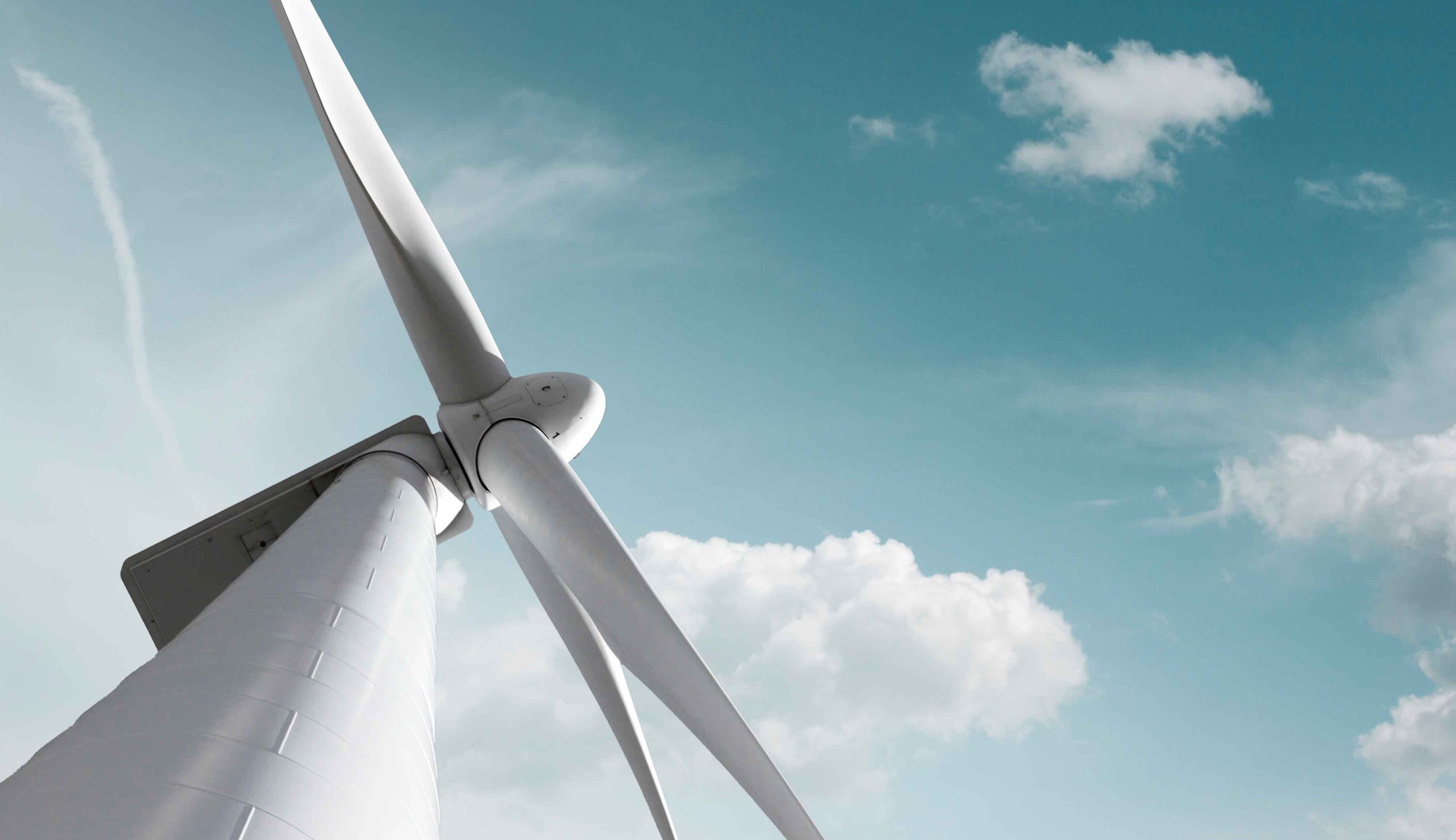


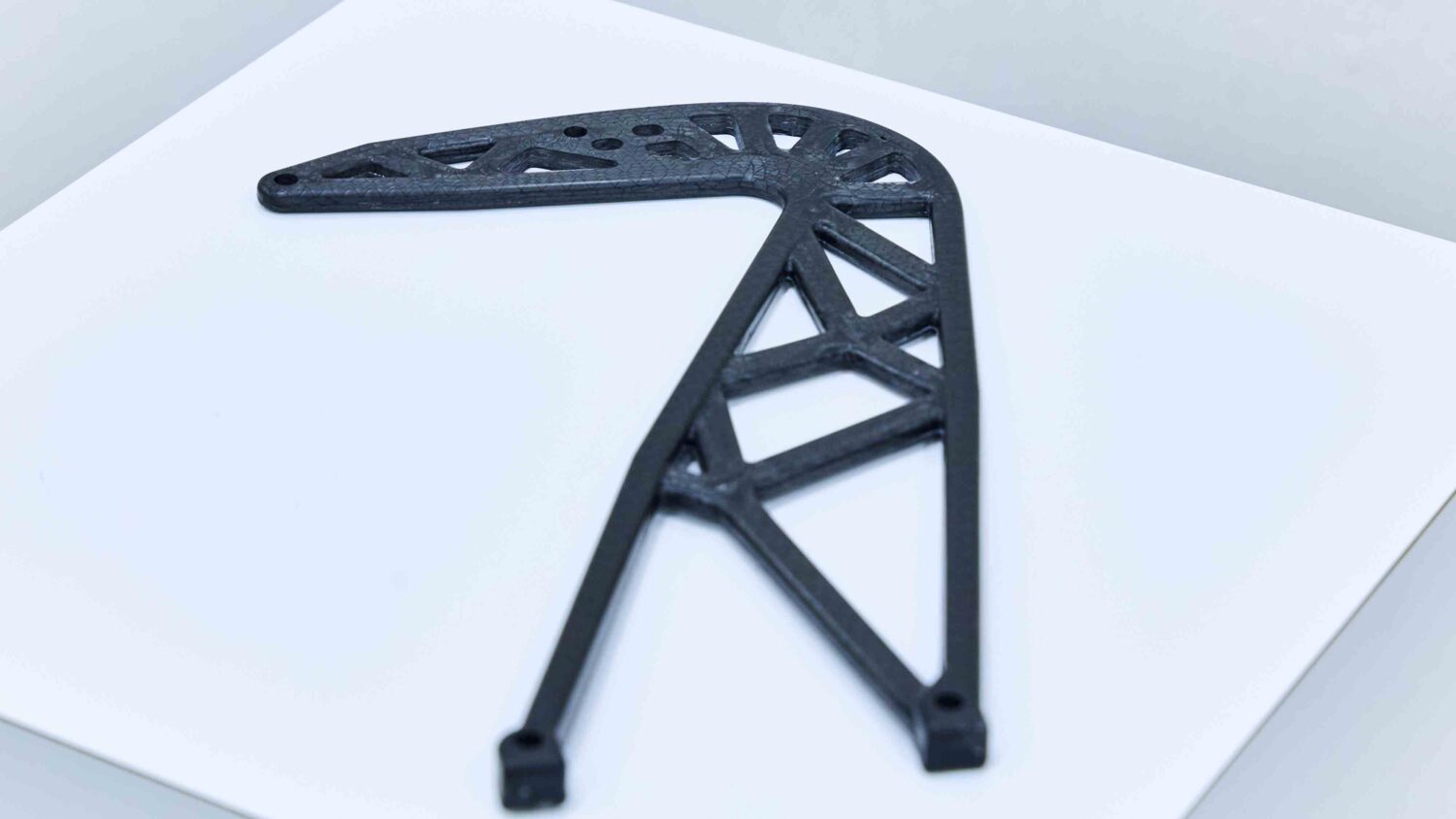
Demand for renewable energy is increasing, as is the scale of wind power generation. We believe the use of carbon fiber reinforced plastics (CFRP) formed using the TFP process have the potential to contribute to even more efficient energy production.
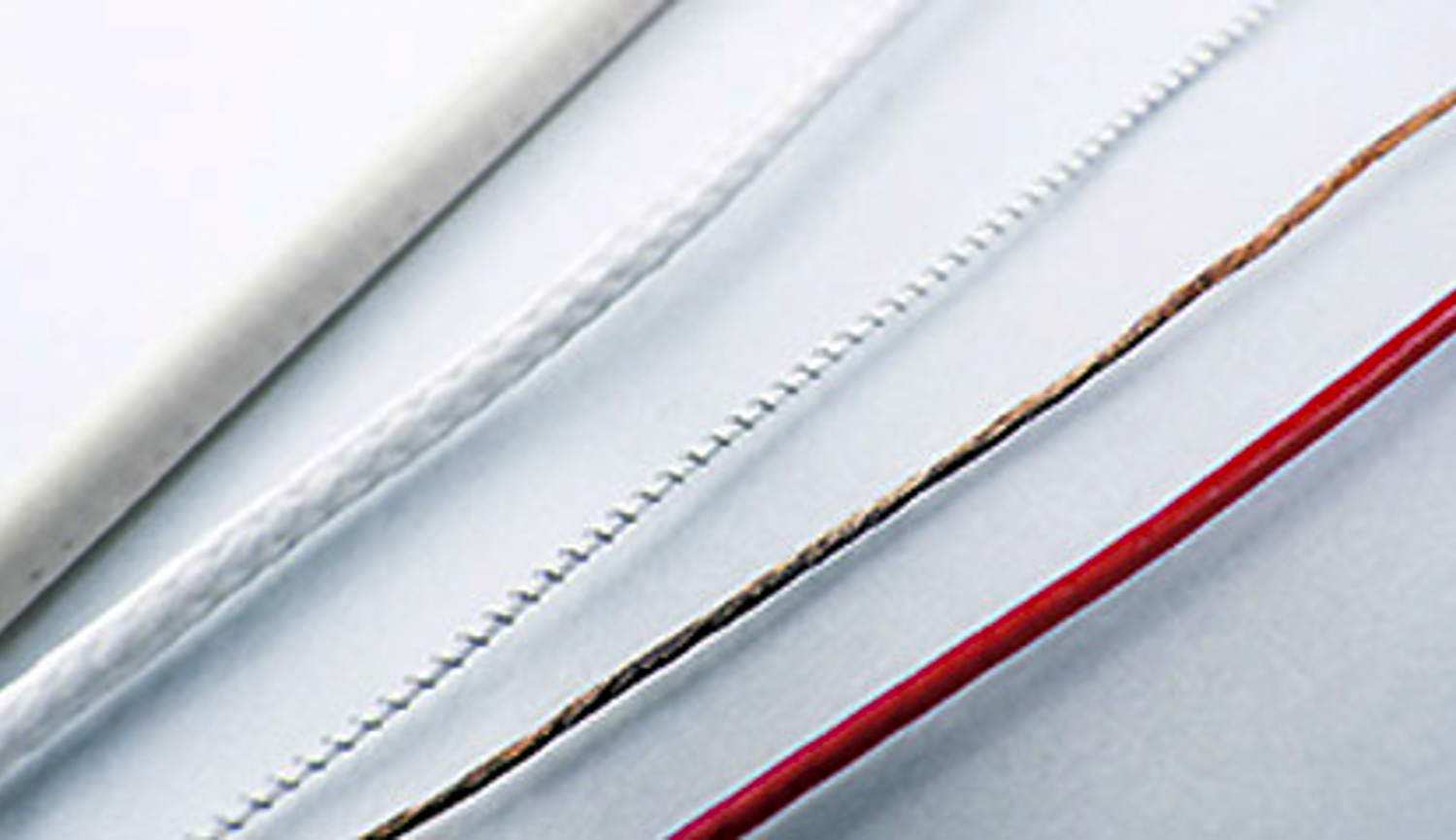


Uses for embroidery technology are seen extending to all sorts of applications, depending on the material including pressure measurements and detecting distortion and temperature. Components can be employed in infrastructure development, disaster prevention, and many other cases.
Support system staffed by specialists
The Tajima Group’s staff of specialists support customers in solving their problems, including development of smart textiles and functional embroidery, and manufacturing, from prototypes to mass production. Please feel free to contact us.
- Those who are considering smart textiles but do not know where to start
- Those who are interested in functional embroidery
- Those facing issues in contributing to the healthcare and infrastructure fields


Recommended Products








